

The left posterior superior temporal gyrus is responsible for the perception of sound, and in itthe primary auditory cortex is the region where the attributes of sound (pitch, rhythm, frequency, etc.) are processed. The primary auditory cortex receives auditory information from the thalamus. The info is then passed to the primary auditory cortex of the brain, situated in the temporal lobe. The neural information ends up at the relay center of the brain, called the thalamus. The cochlear nucleus is the first site of neural processing, followed by the superior olivary complex located in the pons, and then processed in the inferior colliculus at the midbrain. Once the sound waves are turned into neural signals, they travel through cranial nerve VIII, reaching different anatomical structures where the neural information is further processed. The auditory nerve (for hearing) combines with the vestibular nerve (for balance), forming cranial nerve VIII or the vestibulocochlear nerve. Each hair innervates many auditory nerve fibers, and these fibers form the auditory nerve. This organ is comprised of inner hair cells that turn the vibrations into electric neural signals. Analog signals occur in electrical signals. Their frequencies range between 20 to 20,000 Hz, and this is the lower and upper limit of our ears. Audio signals are the representation of sound, which is in the form of digital and analog signals. The cochlear duct contains the organ of Corti. Audio Signal processing is a method where intensive algorithms, techniques are applied to audio signals. The main structure in the inner ear is called the cochlea, where the sensory info in wave form is transformed into the neural form. This segment of the ear is filled with liquid rather than air, that is why there is a need of conversion of low pressure sound vibrations to higher pressure ones in the middle ear. Inner Earīeyond the oval window is the inner ear. These transformed vibrations (still in wave form) enter the oval window. These delicate bones convert the sound vibrations made when the sound waves hit the ear \drum into sound vibrations of higher pressure. The three ossicles include the hammer (malleus), anvil (incus), and stirrup (stapes). Middle EarĪs the sound waves hit the eardrum, the sensory information goes into an air-filled cavity through lever-teletype bones called ossicles.
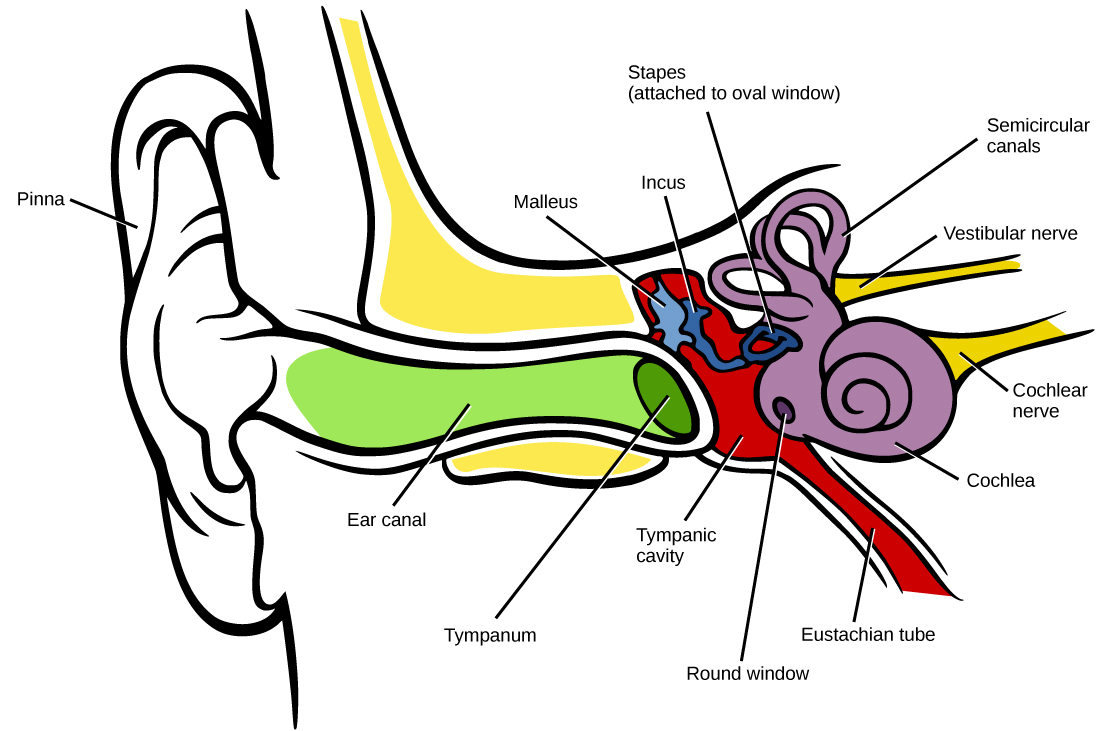

The sound waves travel through the canal and reach the tympanic membrane (eardrum), the canal’s end. From the pinna, the sound waves enter a tube-like structure called auditory canal. The pinna helps the brain identify the direction from where the sounds originated. They surround the ear canal and function as sound wave reflectors and attenuators when the waves hit them. The pinna are the parts of the outer ear that appear as folds of cartilage.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
